SCARA Robot Arm
This project features a custom-built SCARA (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm) designed for precision pick-and-place tasks. The system combines mechanical engineering, embedded programming, and control theory into a single cohesive robotic platform.
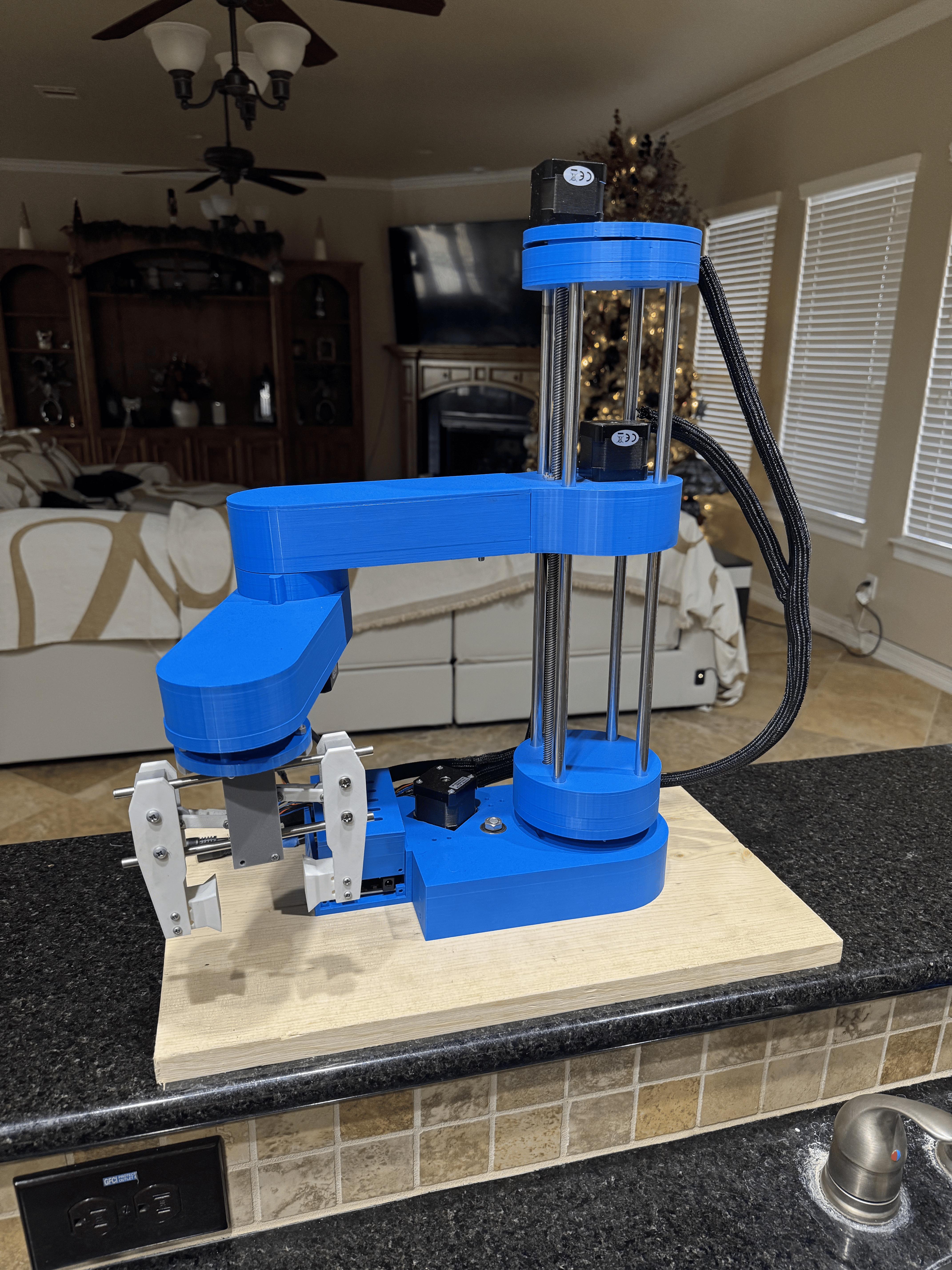
Arduino-Controlled SCARA Robot in Action
- Interfaced with a custom-built control interface developed in Processing.
- Utilizes an Arduino microcontroller for precise motion with forward and inverse kinematics.
- Accepts joint parameters or Cartesian coordinates as input.
- Provides real-time feedback and control over gripper actuation.
- Integrates embedded systems, mechanical design, and user-centered software engineering.
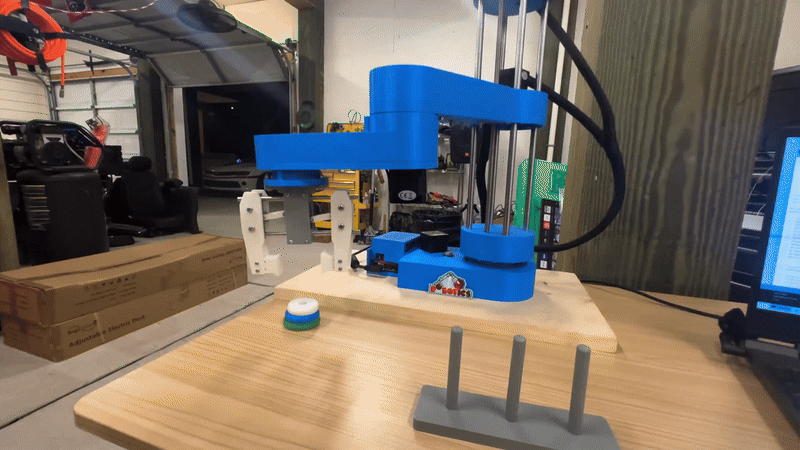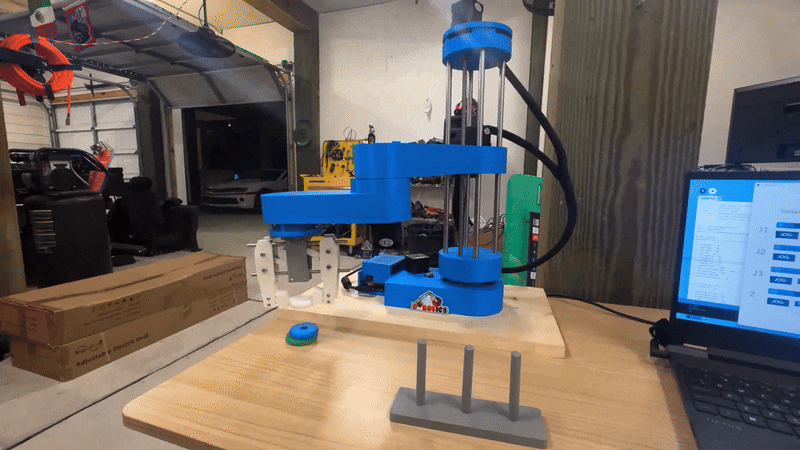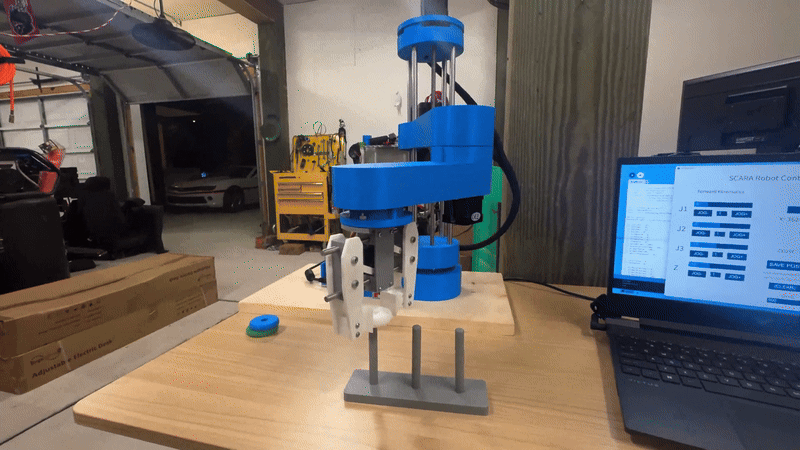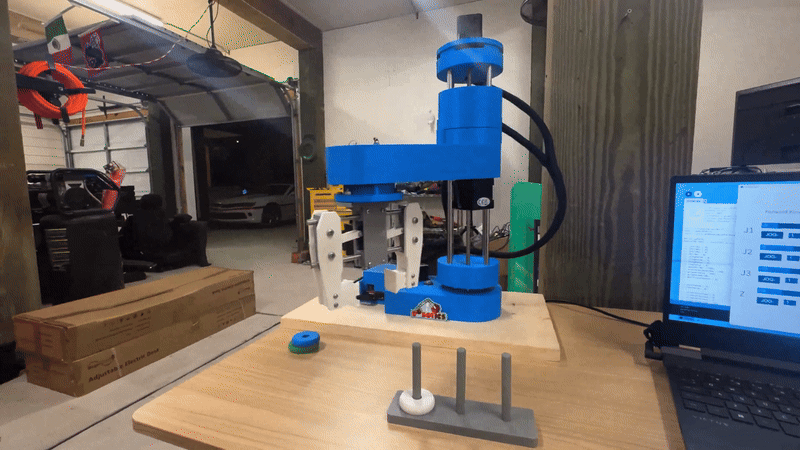
SCARA Robot Performing Pick-and-Place Operation
- Demonstrates precise pick-and-place capabilities using inverse kinematics and PID control.
- Executes high-speed, repeatable motion driven by stepper motors and microcontroller coordination.
- Integrates end-effector control to perform object grasping and placement with accuracy.
- Operates on a pre-programmed motion sequence simulating a production line task.
- Highlights the real-world application of control theory, embedded systems, and motion planning.
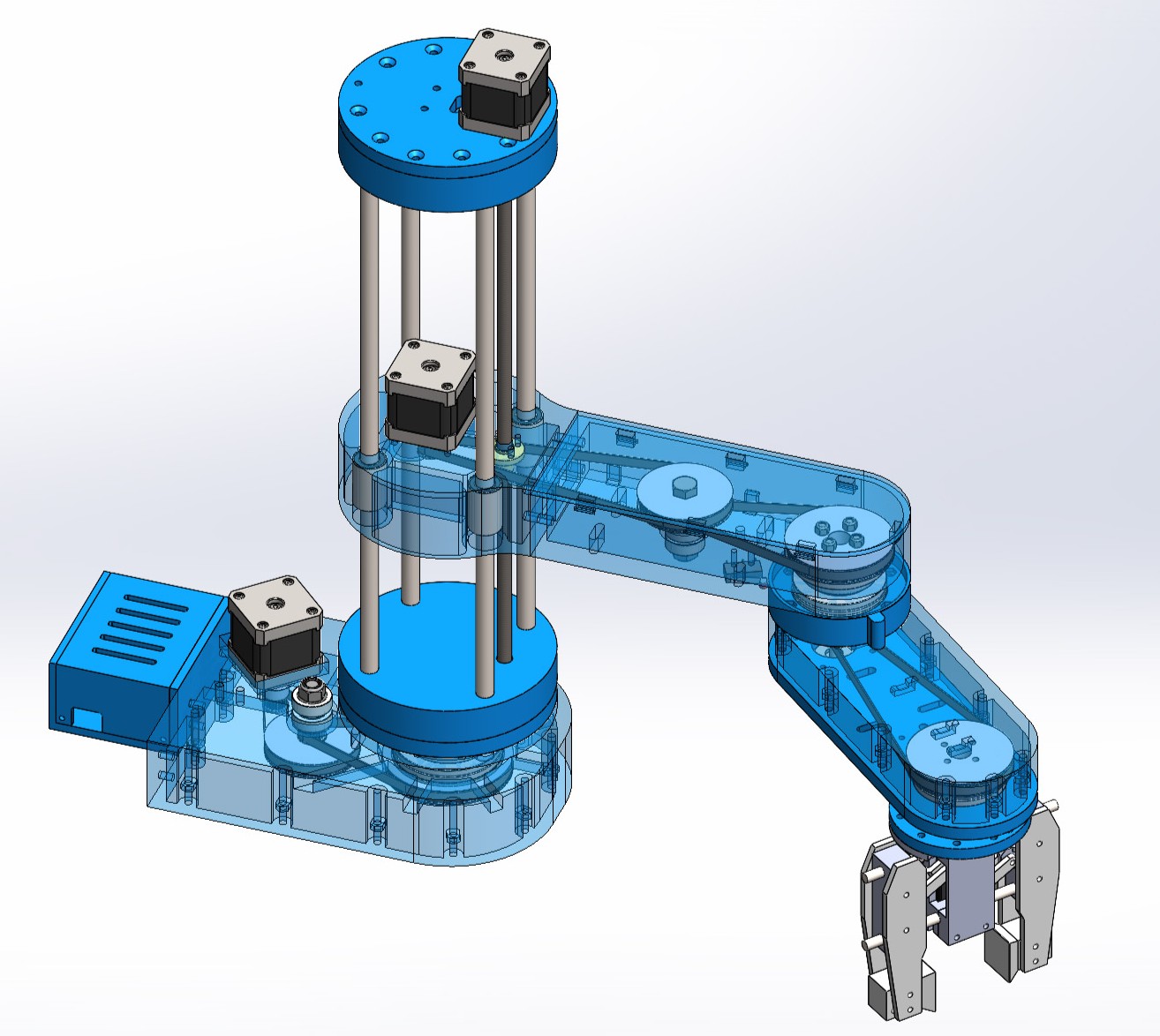
SolidWorks CAD View
- CAD model developed in SolidWorks to visualize mechanical structure and component layout.
- Transparent view highlights internal components such as motors, pulleys, lead screws, and belt systems.
- Designed for modularity, 3D printing, and ease of assembly.
- Emphasizes mechanical design principles including kinematic constraints and actuator alignment.
- Aids in verifying clearances, tolerances, and mechanical integrity prior to physical prototyping.
Tools Used
- Electronics: Arduino Mega, CNC Shield, A4988 stepper drivers, MG996R servo motor, NEMA 17 stepper motors, limit switches, DC power supply (12V/6A)
- 3D Design Software: 3DEXPERIENCE SOLIDWORKS, xDesign, 3DMarkup
- Programming: Arduino IDE (C++), Processing IDE (Java-based), ControlP5 library
- Hardware: Bambu Lab X1 Carbon 3D Printer, PLA/PLA+ filament, linear rods, bearings, lead screws, GT2 pulleys
- Libraries: AccelStepper, ControlP5
Purpose
Design and build a fully functional SCARA robotic arm for educational and experimental purposes, demonstrating core robotics concepts such as kinematics, motion control, and automation.
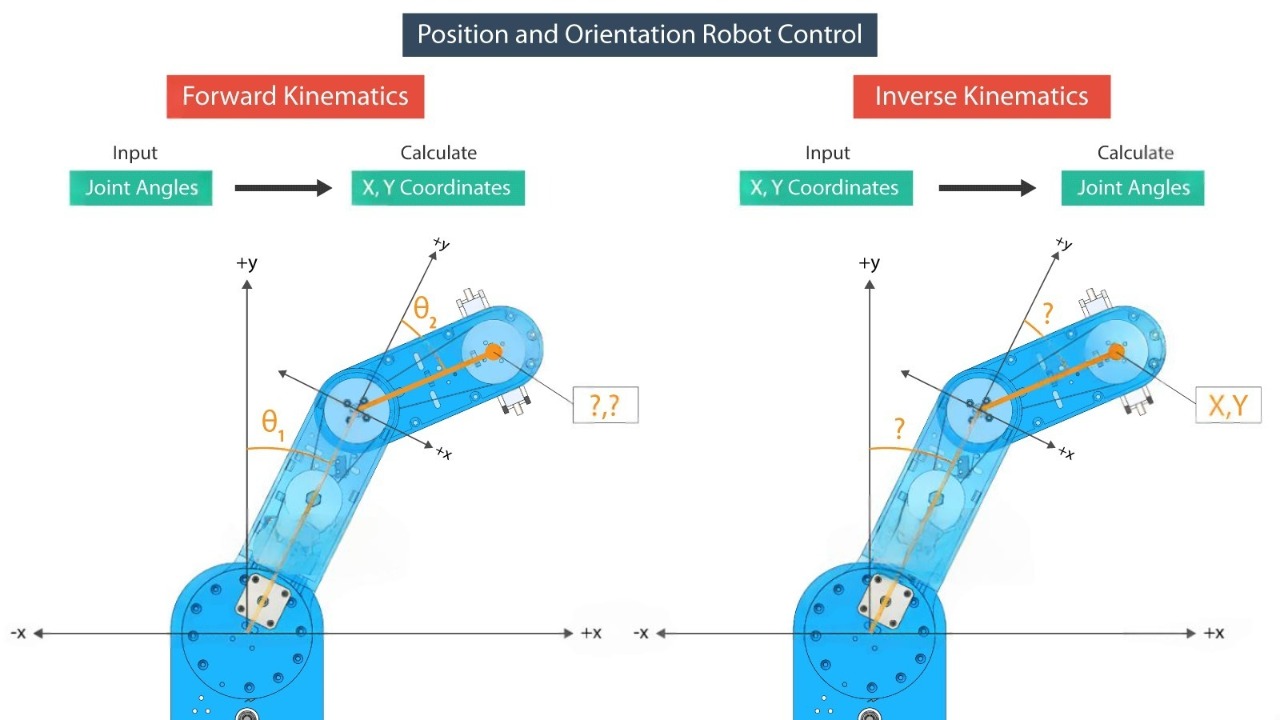
Theory
- Forward Kinematics: Calculates end-effector position from joint angles.
- Inverse Kinematics: Computes joint angles for a specified position.
- Motion Control: Smooth trajectory execution via AccelStepper.
- GUI Integration: Live joint and Cartesian input with visual feedback.
Results
- Demonstrated precise pick-and-place operation using inverse kinematics.
- Manual and automated modes with real-time GUI controls.
- Sequence recording and replay functionality implemented.
- Fully 3D printable modular design using parametric parts.
Conclusion
This SCARA robotic arm project served as a comprehensive demonstration of robotics engineering principles—bringing together CAD modeling, embedded systems, and control algorithms into a functional prototype. Through hands-on integration of hardware and software, the project strengthened practical skills in mechanical design, kinematic theory, and automation. Future improvements, such as integrating computer vision, will further enhance the robot’s autonomy and expand its application potential in industrial and academic settings.
Future Work
- Integrate computer vision for autonomous object detection and tracking.
- Experiment with 3D printing and laser engraving as end-effectors.
- Improve structural rigidity and minimize mechanical backlash.
Simulation & Modeling
- Custom robot models using URDF and Xacro
- Motion control verified through PID tuning in simulation
- Physics-based testing in Gazebo for collision and behavior validation
- Live robot state and path visualization in RViz2

