NASA Lunabotics Autonomous Rover
This project focuses on building and testing an autonomous rover for the NASA Lunabotics competition. My work spans embedded motor control, rover safety behavior, and software integration for differential drive motion using linear and angular velocity commands.
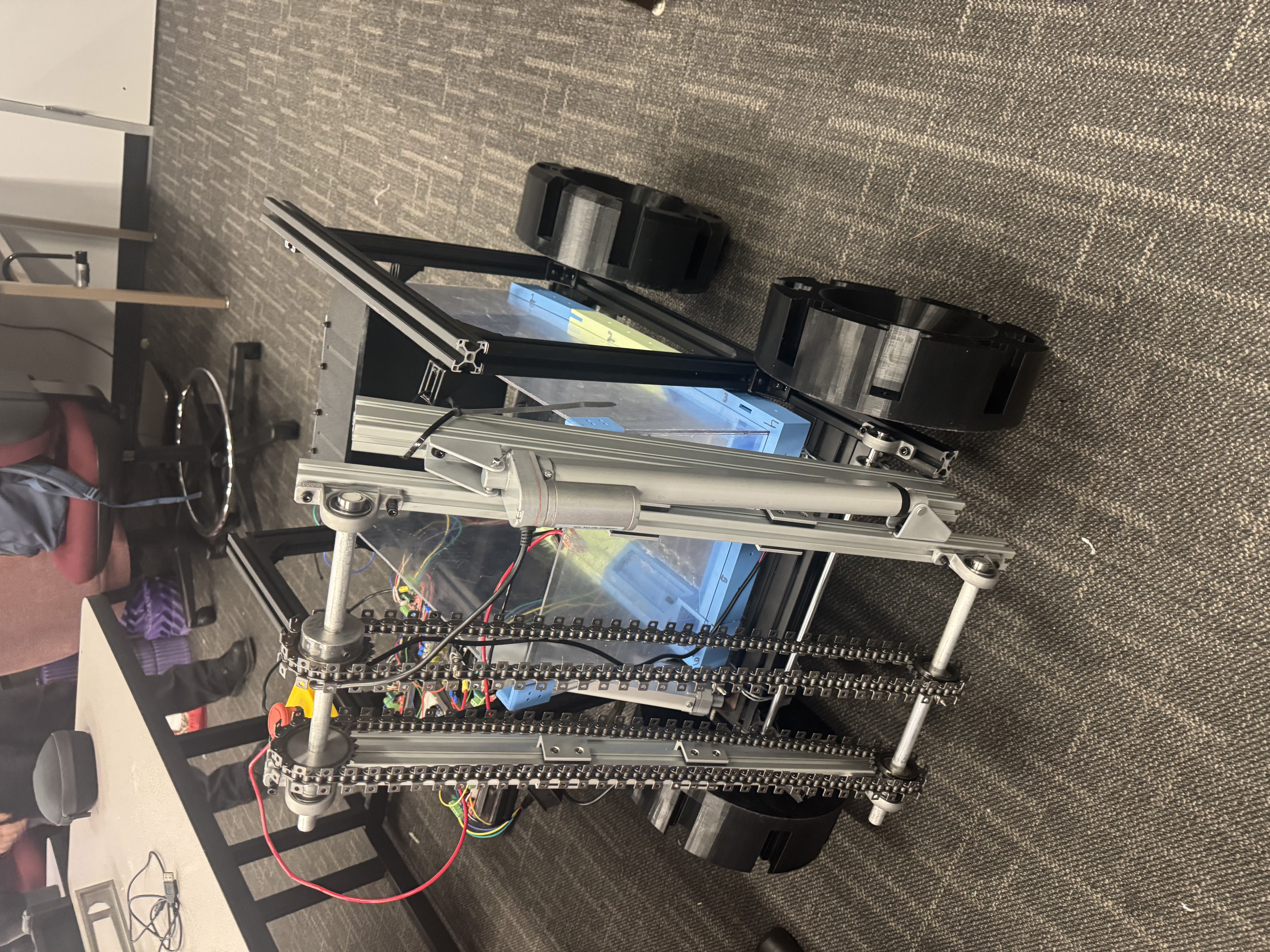
Embedded Control + Rover Safety
- Implemented MicroPython control on ESP32 (WROOM / S3) for rover drive control.
- WebSocket-based control interface that accepts v (linear) and w (angular) commands.
- Differential drive conversion to left/right wheel commands and PWM control.
- Safety behavior on boot: force motor pins LOW to prevent unintended motion.
- Supported testing & debugging of drivetrain behavior and power stability.
Rover Moving Demo
This video demonstrates the Lunabotics rover executing controlled motion during field testing using a velocity-based drive model. The rover is driven through a custom embedded control stack that translates high-level motion commands into low-level motor actuation.
An ESP32 microcontroller (WROOM / S3) runs MicroPython and acts as the primary drive controller. Commands are sent wirelessly from a host system over a WebSocket connection, allowing real-time control and tuning during testing.
- Velocity Command Model: The controller accepts linear velocity (
v) and angular velocity (w) inputs, which are converted into left and right wheel speed commands. - Differential Drive Mapping: Wheel speeds are computed using the rover track width and scaled into PWM outputs for the motor drivers.
- Embedded Safety: On startup and communication loss, all motor control pins are forced LOW to prevent unintended motion.
- Controller Input: Motion commands are issued via a handheld controller interface, enabling smooth throttle response and predictable turning behavior.
Differential Drive with v / w Commands
- Converts linear/angular velocity into left/right wheel commands.
- PWM output (high frequency) to drive motor controllers.
- Safe-stop logic on disconnect or command timeout.
- Tunable constants for turn strength and track width.
- Designed for reliable driving during repeated field testing.

ROS 2 Integration
- ROS 2 used for higher-level autonomy and navigation workflows.
- Clean command pathway supports mapping control inputs into rover motion.
- System designed to expand toward full autonomy over time.
- Debugging focused on repeatable motion + stable power delivery.
Tools Used
- Embedded: ESP32-WROOM, ESP32-S3, MicroPython
- Comms: WebSocket control (microdot + microdot.websocket), Wi-Fi networking
- Robotics: Differential drive, v/w command model
- Software: ROS 2, Linux
- Testing: Power + drivetrain debugging during field testing
Purpose
Contribute to a competition-ready rover platform by delivering a reliable embedded control stack, safe startup behavior, and a clean interface for higher-level robotics software.
Results
- Stable remote driving using v/w velocity commands.
- Safety boot behavior prevents accidental movement at startup.
- Improved repeatability during drivetrain testing.
- Foundation created for future autonomy integration.
Future Work
- Sensor integration for autonomy (encoders / IMU / LiDAR).
- ROS 2 navigation improvements and better state estimation.
- More robust power distribution and load testing.

